Drive Partitions: What Exactly Are They?
The word “Partition” seems to come from the root word “Part” which means a fraction or a particular section of a given whole. This means that a hard disk partition represents a specified fraction of your computer’s hard disk space which is created for a specific purpose.
But being part or fraction of your computer’s hard disk does not always meant that a partition is less than 100 percent of your drive’s total storage capacity. A partition can actually compose the whole hard disk space and a hard drive can still exist even if it does not have any partition on it. However, if this happens, it won’t be able to designate certain parts of your computer’s hard disk space for certain purpose like Booting or storing System files needed for your machine to start properly every time.
What’s the Use of Partitions
Drive partitioning has a lot of uses but for this tutorial, we will just be focusing on the storage use and not more on the technical side of these things. A hard disk partition can be used as storage for important files or more commonly referred to as a “Backup” so you can keep all crucial documents and other stuff in a place that is separate from the partition where your operating system is installed. This is a good way of securing files from being lost or damaged once a troubles and other major problems occur on your machine’s primary partition containing the operating system. Another use is for storing files that you want to enable for sharing to other users on your network. This can apply to network sharing features like the HomeGroup on Windows 7 and Windows 8. Putting all shared files in one partition helps avoid confusion and spares you from any wasted time just in searching and identifying files that are shared to other users on your network. Lastly, a hard disk partition can also hold another operating system so you can have a “dual-boot” system. For instance, if you are using Windows 7 and you want to try Windows 8 first before you decide to upgrade then you can do it by installing trial version of Windows 8 on a separate partition. Once this is done, your system will alert you to choose between Windows 7 and Windows 8 each time you turn on your computer.
Partition Types
There are two types of partitions which can be made on your computer’s hard drive. What to use in certain situations all depends on what your purpose is in creating the space on your disk. The type of partition may also differ depending on the operating system installed on your computer and the file system format that is used in it. I will be explaining more about these two types of partition below. Just continue reading so you can learn how one differs from the other.
Extended Partitions
An Extended partition is tagged in dark green. This type of partition is capable of holding multiple logical drives in it. Below are things that you need to remember and as well as screenshots showing an Extended partition.
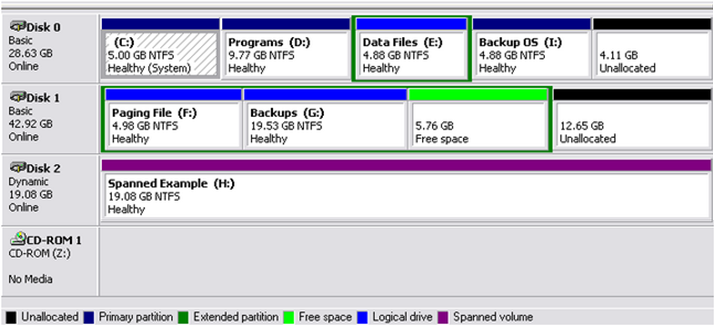
- The screenshot below shows some partitions having a dark green band around. These are examples of logical drives contained within an Extended partition. Remember that the dark green color denotes an Extended partition and in most cases, you will see drives and partitions having different colors but are surrounded or enclosed together by a dark green band.

- Extended partitions are never given a drive letter or even formatted.
The screenshot below shows what the drive and partition color labels/tags mean. This legend is found at the bottom of the Disk Manager Window. As you can see, the dark green color label means that a partition is an Extended one.
![]()
Primary Partitions
As shown on the screenshot above, a Primary partition is denoted by the dark blue color label. This type of partition bears all the important files and stuff including the operating system itself. Other partitions can also be created from it and contain important System and Boot files needed by the OS to start properly every time you turn on your machine. The screenshot below shows a primary partition.

To clearly illustrate what partitions are, I took the time to create a sample of each one of them and took a screenshot of everything as shown below.
Note:
- A maximum of four Primary partitions can be created from your computer’s hard disk and the size of each one depends on the remaining free space that your computer still has. If you have two hard disks (the one that is built-in and an external drive), you can have up to 8 Primary partitions.
- It is not necessary for a Primary partition to be listed first or precede an Extended partition as illustrated by Disk 0 on the screenshot above.
- A hard drive does not necessarily need a Primary partition as shown by Disk 1 above
- If you have a blank CD/DVD on your computer’s CD-ROM drive, it will always appear to have nothing in it, no partitions, files etc.
Logical Partitions/Drives
As I mentioned above, Extended partitions can contain logical drives within them. A logical drive is marked by a bright-blue color label and are most of the time surrounded by a dark green band as shown on the screenshot below.

Note:
- An unlimited number of logical drives can be created within an Extended partition but “Unlimited” does not mean endless. You are also limited either by the amount of storage space that your hard disk still has and the drive letters that you can assign to each logical drives. Once the space runs out or all drive letters are already used, you can anymore create a logical drive. The Screenshot below shows Drive F: and G: as well as a a Free space having no drive label contained within an Extended drive. You will know that it is within an extended drive because of the dark green band surrounding the drives.

What’s the Difference Between a System and a Boot Partition?
People are often confused between the a System and a Boot partition but on this section, I will do my best to explain what each one is and what it is used for so you can know what to do when you encounter these type of partitions.
Both System and Boot Partitions are very important to your computer’s Operating System and without it, your machine will be utterly useless because it will not start up the way that it does earlier when you turned on your computer.
- System Partition- Whether you want to do a cold boot by long-pressing your computer’s power button or a warm boot simply by restarting it, the system partition is very much needed since it holds all the needed files and system information needed for your computer to boot properly.
- Boot Partition- After the first step is done and all files and information from the System partition is executed, your machine will then need to access the Boot partition which contains all system files needed for the operating system to start completely.
Both partitions work hand-in-hand to accomplish one task which is to bring you to the desktop or the log-on screen of your computer.
- Active Partition- You may also see a drive that has a description saying “Active Partition”. This actually means the same as a System Partition or the space where your computer’s operating system is installed.
Knowing how one partition/drive differs from the other will help you identify which ones are safe to delete, shrink or extend. More about these steps will be described and illustrated further on the coming tutorials. If you have questions regarding the topic described on this article please feel free to post them as comments below.